Understanding Septal Infarct: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
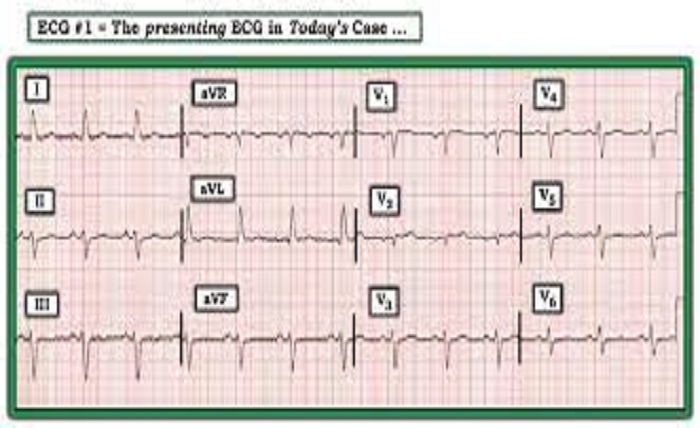
Septal infarct is a medical condition characterized by damage or injury to the septum, the wall that separates the left and right ventricles of the heart. This condition is often associated with a heart attack, where a blockage in one of the coronary arteries restricts blood flow to the heart muscle. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for septal infarct, shedding light on this important cardiovascular condition.
Understanding Septal Infarct:
Septal infarct occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the septum, leading to tissue damage and necrosis. The septum plays a vital role in maintaining the separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart. When the blood supply is compromised, the affected area of the septum may lose its ability to function properly, impacting overall cardiac performance.
Causes of Septal Infarct:
The most common cause of septal infarct is a coronary artery blockage due to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Plaque buildup narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow to the heart. Other causes include blood clots, emboli, and vasospasm, which can also result in decreased blood supply to the septum and subsequent infarction.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Symptoms of septal infarct may vary depending on the extent and location of the damage. Some common signs include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and lightheadedness. Diagnostic procedures such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and coronary angiography are commonly used to detect septal infarct and assess its severity.
Complications and Prognosis:
Septal infarct can lead to various complications, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and ventricular septal defects (VSDs). The prognosis for individuals with septal infarct depends on factors such as the size of the infarction, the promptness of treatment, and the overall cardiovascular health of the patient. Timely medical intervention and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve the prognosis.
Treatment Options:
The primary goal of treating septal infarct is to restore blood flow to the affected area and prevent further damage. Prompt medical intervention is crucial, and treatment options may include medications such as thrombolytics, antiplatelet drugs, and beta-blockers to reduce clotting, improve blood flow, and manage symptoms. In severe cases, surgical interventions like percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be necessary.
Rehabilitation and Lifestyle Modifications:
After the initial treatment, rehabilitation plays a vital role in the recovery process. Cardiac rehabilitation programs help patients regain strength, improve cardiovascular health, and make necessary lifestyle modifications. This may involve supervised exercise programs, dietary changes, stress management, and smoking cessation.
Preventive Measures:
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of septal infarct and other cardiovascular diseases. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding smoking can significantly lower the chances of developing septal infarct. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor cardiovascular health and identify any potential risk factors.
Conclusion:
Septal infarct is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for septal infarct can empower individuals to seek timely intervention and make necessary lifestyle modifications. By prioritizing cardiovascular health, we can reduce the risk of septal



